Java Jdbc Driver Types

Java JDBC has 4 different database driver types, and this text explains the difference between them.
A JDBC driver is a software component enabling a Java application to interact with a database. 1 JDBC drivers are analogous to ODBC drivers, ADO.NET data providers, and OLE DB providers.
To connect with individual databases, JDBC the Java Database Connectivity API requires drivers for each database. The JDBC driver gives out the connection to the database and implements the protocol for transferring the query and result between client and database.
JDBC technology drivers fit into one of four categories. 2
Network-Protocol driver Middleware driver
Database-Protocol driver Pure Java driver
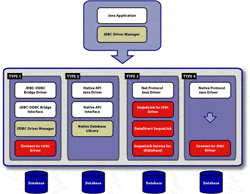
1 Type 1 driver – JDBC-ODBC bridge
2 Type 2 driver – Native-API driver
3 Type 3 driver – Network-Protocol driver middleware driver
4 Type 4 driver – Database-Protocol driver Pure Java driver
Type 1 driver – JDBC-ODBC bridge edit
Schematic of the JDBC-ODBC bridge
The JDBC type 1 driver, also known as the JDBC-ODBC bridge, is a database driver implementation that employs the ODBC driver to connect to the database. The driver converts JDBC method calls into ODBC function calls.
The driver is platform-dependent as it makes use of ODBC which in turn depends on native libraries of the underlying operating system the JVM is running upon. Also, use of this driver leads to other installation dependencies; for example, ODBC must be installed on the computer having the driver and the database must support an ODBC driver. The use of this driver is discouraged if the alternative of a pure-Java driver is available. The other implication is that any application using a type 1 driver is non-portable given the binding between the driver and platform. This technology isn t suitable for a high-transaction environment. Type 1 drivers also don t support the complete Java command set and are limited by the functionality of the ODBC driver.
Sun provided a JDBC-ODBC Bridge driver: sun.jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver. This driver is native code and not Java, and is closed source. Oracle s JDBC-ODBC Bridge was removed in Java 8 other vendors are available. 3 4
If a driver has been written so that loading it causes an instance to be created and also calls DriverManager.registerDriver with that instance as the parameter as it should do, then it is in the DriverManager s list of drivers and available for creating a connection.
It may sometimes be the case that more than one JDBC driver is capable of connecting to a given URL. For example, when connecting to a given remote database, it might be possible to use a JDBC-ODBC bridge driver, a JDBC-to-generic-network-protocol driver, or a driver supplied by the database vendor. In such cases, the order in which the drivers are tested is significant because the DriverManager will use the first driver it finds that can successfully connect to the given URL.
First the DriverManager tries to use each driver in the order it was registered. The drivers listed in jdbc.drivers are always registered first. It will skip any drivers that are untrusted code unless they have been loaded from the same source as the code that is trying to open the connection.
It tests the drivers by calling the method Driver.connect on each one in turn, passing them the URL that the user originally passed to the method DriverManager.getConnection. The first driver that recognizes the URL makes the connection.
Almost any database for which an ODBC driver is installed can be accessed, and data can be retrieved.
Performance overhead since the calls have to go through the JDBC bridge to the ODBC driver, then to the native db connectivity interface thus may be slower than other types of drivers.
The ODBC driver needs to be installed on the client machine.
Not suitable for applets, because the ODBC driver needs to be installed on the client.
Type 2 driver – Native-API driver edit
Schematic of the Native API driver
The JDBC type 2 driver, also known as the Native-API driver, is a database driver implementation that uses the client-side libraries of the database. The driver converts JDBC method calls into native calls of the database API. For example: Oracle OCI driver is a type 2 driver.
As there is no implementation of JDBC-ODBC bridge, its considerably faster than a type 1 driver.
The vendor client library needs to be installed on the client machine.
Not all databases have a client side library.
This driver is platform dependent.
This driver supports all java applications except applets.
Type 3 driver – Network-Protocol driver middleware driver edit
Schematic of the Network Protocol driver
The JDBC type 3 driver, also known as the Pure Java driver for database middleware, 5 is a database driver implementation which makes use of a middle tier between the calling program and the database. The middle-tier application server converts JDBC calls directly or indirectly into the vendor-specific database protocol.
This differs from the type 4 driver in that the protocol conversion logic resides not at the client, but in the middle-tier. Like type 4 drivers, the type 3 driver is written entirely in Java.
The same driver can be used for multiple databases. It depends on the number of databases the middleware has been configured to support. The type 3 driver is platform-independent as the platform-related differences are taken care of by the middleware. Also, making use of the middleware provides additional advantages of security and firewall access.
Sends JDBC API calls to a middle-tier net server that translates the calls into the DBMS-specific network protocol. The translated calls are then sent to a particular DBMS.
Follows a three tier communication approach.
Can interface to multiple databases – Not vendor specific.
The JDBC Client driver written in java, communicates with a middleware-net-server using a database independent protocol, and then this net server translates this request into database commands for that database.
Thus the client driver to middleware communication is database independent.
Since the communication between client and the middleware server is database independent, there is no need for the database vendor library on the client. The client need not be changed for a new database.
The middleware server which can be a full-fledged J2EE Application server can provide typical middleware services like caching of connections, query results, etc., load balancing, logging, and auditing.
A single driver can handle any database, provided the middleware supports it.
Requires database-specific coding to be done in the middle tier.
The middleware layer added may result in additional latency, but is typically overcome by using better middleware services.
Type 4 driver – Database-Protocol driver Pure Java driver edit
Schematic of the Native-Protocol driver
The JDBC type 4 driver, also known as the Direct to Database Pure Java Driver, is a database driver implementation that converts JDBC calls directly into a vendor-specific database protocol.
Written completely in Java, type 4 drivers are thus platform independent. They install inside the Java Virtual Machine of the client. This provides better performance than the type 1 and type 2 drivers as it does not have the overhead of conversion of calls into ODBC or database API calls. Unlike the type 3 drivers, it does not need associated software to work.
As the database protocol is vendor specific, the JDBC client requires separate drivers, usually vendor supplied, to connect to different types of databases. This type includes, for example, the widely used Oracle thin driver.
Completely implemented in Java to achieve platform independence.
These drivers don t translate the requests into an intermediary format such as ODBC.
The client application connects directly to the database server. No translation or middleware layers are used, improving performance.
The JVM can manage all aspects of the application-to-database connection; this can facilitate debugging.
Drivers are database dependent, as different database vendors use widely different and usually proprietary network protocols.
List of jdbc vendors registered with Oracle
List of drivers registered with Oracle
Open Source Performance Benchmark
Open Database Connectivity ODBC
Java SE Technologies - Database
Oracle. JDBC-ODBC Bridge. https://docs.oracle.com/. Retrieved 27 June 2015.
Retrieved from https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php.title JDBC_driver oldid 685622517
Categories: Java platformData access technologies.

JDBC drivers are divided into four types or levels. The different types of jdbc drivers are: Type 1: JDBC-ODBC Bridge driver Bridge Type 2: Native-API/partly Java.
are divided into four types or levels. The
different types of jdbc drivers are:
Type 1: JDBC-ODBC Bridge driver Bridge
Type 2: Native-API/partly Java driver Native
Type 3: AllJava/Net-protocol driver Middleware
Type 4: All Java/Native-protocol driver Pure
4 types of jdbc drivers are elaborated in detail as shown below:Type 1 JDBC Driver
The Type 1 driver translates all JDBC calls into ODBC calls and sends them to the ODBC driver. ODBC is a generic API. The JDBC-ODBC
Bridge driver is recommended only for experimental use or when no other alternative is available.
The JDBC-ODBC Bridge allows access to almost any database, since the database s ODBC drivers are already available.
1. Since the Bridge driver is not written fully in Java, Type 1 drivers are not portable.
2. A performance issue is seen as a JDBC call goes through the bridge to the ODBC driver, then to the database, and this applies even in
the reverse process. They are the slowest of all driver types.
3. The client system requires the ODBC Installation to use the driver.
4. Not good for the Web.Type 2 JDBC Driver
The distinctive characteristic of type 2 jdbc drivers
are that Type 2 drivers convert JDBC calls into database-specific calls i.e. this driver is specific to a particular database.
Some distinctive characteristic of type 2 jdbc drivers
are shown below. Example: Oracle will
Type 2: Native api/ Partly Java Driver
The distinctive characteristic of type 2 jdbc drivers are
that they are typically offer better performance than the JDBC-ODBC Bridge as the layers of communication tiers are less than that of Type
1 and also it uses Native api which is Database specific.
1. Native API must be installed in the Client System and hence type 2 drivers cannot be used for the Internet.
2. Like Type 1 drivers, it s not written in Java Language which forms a portability issue.
3. If we change the Database we have to change the native api as it is specific to a database
Type 3 database requests are passed through the network to the middle-tier server. The middle-tier then translates the request to the database.
If the middle-tier server can in turn use Type1, Type 2 or Type 4 drivers.
Type 3: All Java/ Net-Protocol Driver
1. This driver is server-based, so there is no need for any vendor database library to be present on client machines.
2. This driver is fully written in Java and hence Portable. It is suitable for the web.
3. There are many opportunities to optimize portability, performance, and scalability.
4. The net protocol can be designed to make the client JDBC driver very small and fast to load.
5. The type 3 driver typically provides support for features such as caching connections, query results, and so on, load balancing, and advanced
system administration such as logging and auditing.
6. This driver is very flexible allows access to multiple databases using one driver.
7. They are the most efficient amongst all driver types.
It requires another server application to install and maintain. Traversing the recordset may take longer, since the data comes through the backend server.
Native-protocol/all-Java driver
The Type 4 uses java networking libraries to communicate directly with the database server.
Type 4: Native-protocol/all-Java driver
1. The major benefit of using a type 4 jdbc drivers are
that they are completely written in Java to achieve platform independence and eliminate deployment administration issues. It is most suitable
2. Number of translation layers is very less i.e. type 4 JDBC drivers don t have to translate database requests to ODBC or a native connectivity interface
or to pass the request on to another server, performance is typically quite good.
3. You don t need to install special software on the client or server. Further, these drivers can be downloaded dynamically.
With type 4 drivers, the user needs a different driver for each database.
The JDBC type 2 driver, also known as the Native-API driver, is a database driver implementation that uses the client-side libraries of the database.
This page contains information about Java Database Connectivity JDBC related to Java SE.
Java Database Connectivity JDBC is an application programming interface API for the programming language Java, that defines how a client may access a database.
JDBC Driver Types- Learning JDBC in simple and easy steps using this beginner s tutorial containing basic to advanced knowledge of JDBC including Drivers.